
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation: Conjugate base for each below acid should be determined. Also, rank of conjugate bases from strongest to weakest P.E. should be determined.
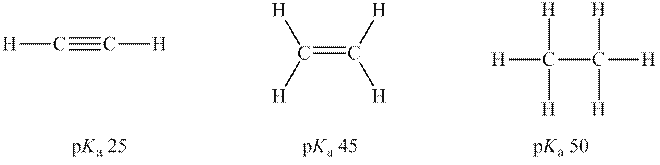
Concept introduction: According to the Bronsted-Lowry concept, a substance that donates proton is termed as acid while that accepts or gains protons is called a base. Species formed after loss of protons from acids are known as their respective conjugate bases whereas conjugate acid is produced by the addition of protons to base. The strength of conjugate acids and conjugate bases are inversely related to strengths of their respective bases and acids.
According to Lewis's concept, a substance that donates electron pair is termed as a base while that accepts or gains electron pair is called acid. For example,
According to the Arrhenius concept, substances that donate hydrogen ions in solutions are known as acids while bases are substances that release hydroxide ions in solutions.
b)
Interpretation: Type of orbital that has a lone pair of electrons in the below conjugate base should be drawn.
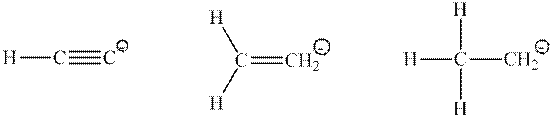
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to the different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
c)
Interpretation: Percent
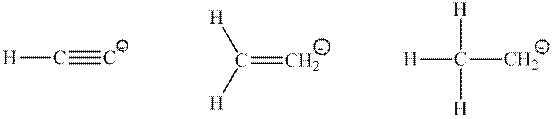
Concept introduction: Hybridization is processed to intermix atomic orbitals in order to form new hybrid orbitals. It can be determined by the calculation of the number of hybrid orbitals
Type of hybridization that corresponds to a different number of hybrid orbitals is described in the following table:
d)
Interpretation: Whether
Concept introduction: Orbitals are defined as regions around atomic nucleus where electrons are found. Atomic orbitals help to form covalent bonds. Atomic orbitals can be
e)
Interpretation: Reason for pattern in
Concept introduction:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
- For each molecule below, draw the conjugate acid or conjugate base or both if the molecule hasboth a conjugate acid and a conjugate base (e.g., water).arrow_forwardFCH₂ NAZ Z c dentify the Conjugat base protons (labeled H₂- it HA N/H₂ CHICH, NHÀ H 5) Rink. He following order (HD) in Explain using ARIO H₂ HBarrow_forward9. For each pair of molecules, circle the stronger base. Use pKa values to guide your decisions. b. o a. C. d. HO-H N.arrow_forward
- a. Which of the acids in the table above has the strongest conjugate base? b. What is the structure of the strongest acid in the table above?arrow_forwardwhich of the following molecules would be the strongest base, and which would be the weakest base? NH A. B C D. a. C - strongest base, and D - weakest base b. C - strongest base, and B - weakest base C. A - strongest base, and D - weakest base d. D- strongest base, and A - weakest base e. B - strongest base, and Cweakest base f. D- strongest base, and C- weakest basearrow_forwardWhat is the conjugate base of HSO4- is ???? a. SO4 2- b. H2SO4 c. H3O+ d. None correctarrow_forward
- 2. Which structure is the stronger acid, A or B? Explain your answer. F Br Aarrow_forward1. Which of the following compounds is most acidic? a. I b. Il с. ||| d. IV e. V I ОН II ОН Br III ОН Br Br IV ОН V F ОНarrow_forward3. Rank the acidity of the labeled protons in the following molecule from lowest to highest acidity. Explain your answer to get credit. Hc. NHaarrow_forward
- 5) Circle the most acidic hydrogen and put a square around the most basic site in each of the following compounds. Draw the atom out if it is not explicit. B. C. HO HO-S- 11 NH₂ A. -OH E. F. D. -OH -OH OH 5arrow_forward4 5. Rank the following molecules in order of increasing acidity of the most acidic proton in each. You can always look for similar structures on the pK, table to help you out! alle ohl A All CCl3arrow_forward23. Rank the following bases from LEAST BASIC TO MOST BASIC: CI, F, NH₂, OH A) CF < F< OH < NH₂ B) CI < F< NH₂arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
