
Concept explainers
The picture of the spaceships and shuttle from the previous page is reproduced at right.
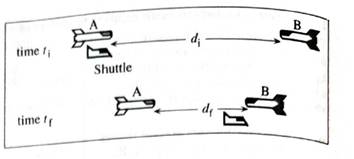
The diagram below the picture shows the positions of the two spaceships and the shuttle at time
Diagram for reference frame of spaceships A
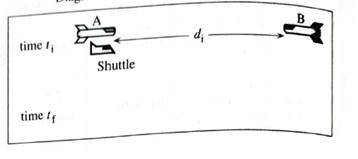
Sketch spaceships A, B, and the shuttle at their positions at time
In the box at right, draw and labelvectors for

Describe how you could use
Is the magnitude of the velocity of the shuttle in the frame of spaceship A greater than, less than, or equal to the magnitude of the velocity of the shuttle in the frame of spaceship B? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
College Physics (10th Edition)
- The Vehicle stands at point [2,1]’ and theta angle 30degree on World frame. The sensormounted at [1,0]’ point on Vehicle. The sensor has detected an obstacle at point [1,-1]’ onSensor frame.a. Firstly calculate from the sensor frame to the Word frame Homegenoustransformation Matrix step by step.b. Find the obstacle position on World frame?arrow_forwardCan you solve this without the transformation matrix and if thtas not possible explain what they do. Also can you explain why you need to change from the J2000 state to geocentric equatorial frame. also would this code work to solve the problem?: % Step 1: Define the initial state vector at burnout r0 = [5210.345121, -549.481941, 4300.883291]; % Position vector [km] v0 = [-1.451280 7.391098 2.690198]; % Velocity vector [km/s] % Step 2: Calculate the initial velocity magnitude and specific angular momentum v0_mag = norm(v0); % Initial velocity magnitude [km/s] h0 = cross(r0, v0); % Specific angular momentum vector [km^2/s] h0_mag =…arrow_forwardIn a frame at rest with respect to the billiard table, two billiard balls of same mass m are moving toward each other with the same speed v. After the collision, the two balls come to rest. (a) Show that momentum is conserved in this frame. (b) Now, describe the same collision from the perspective of a frame that is moving with speed v in the direction of the motion of the first ball. (c) Is the momentum conserved in this frame?arrow_forward
- What is the velocity of an electron that has a momentum of 3.04×10-21?kg·m/s? Note that you must calculate the velocity to at least four digits to see the difference from c.arrow_forwardEinstein observed an explosion at (4.0 [m] ,7.0 [m]). Schrödinger moves to the left with speed 0.75 relative to Einstein. What is the time and the location in space of the explosion according to Schrödinger? Draw a two- body spacetime diagram with Einstein as the laboratory frame observer and Schrödinger as the rocket frame observer. Indicate the explosion in the diagram. 1983arrow_forwardA light source G is moving, with respect to an observer O, at an angle 0 =117° between the direction of relative motion and the line of sight from O to G. The redshift of the light emitted by G and measured by O is z = 0. Find the speed of G with respect to O in units of c, the speed of light. Enter your answer to 3 decimal places. direction of relative motion G line of sightarrow_forward
- Draw it. . At t = 0 a person on earth sends a light signal to a researcher on a rocket, the signal is reflected on the rocket and then destected by the person. How should the space time diagram look like? From the persepective of the observer on the earth?arrow_forwardI need only number 1 and 2 revise. The red color comment is written by my professor. *Please write your explain and tell me where I'm wrong and what did you change. Thank you 1. A rocket is moving at 1/4 c relative to Earth. At the center of this rocket, a light source suddenly flashes. To an observer at rest in the rocket a. the light pulse will reach the front of the rocket at the same instant that it reaches the back of the rocket. b. the light pulse will reach the front of the rocket before it reaches the back of the rocket. c. the light pulse will reach the front of the rocket after it reaches the back of the rocket. 2. A rocket is moving at 1/4 c relative to Earth. At the center of this rocket, a light source suddenly flashes. To an observer at rest on Earth a. the light pulse will reach the front of the rocket at the same instant that it reaches the back of the rocket. b. the light pulse will reach the front of the rocket before it reaches the back of the rocket. c. the light…arrow_forwardPlease answer this; readable and handwriting pls. Please indicate what given and the symbols. And how the formula change and etc LENGTH CONTRACTION A particle is traveling through the Earth’s atmosphere at a speed of 0.750c. To an Earth-bound observer, the distance it travels is 2.50km. How far does the particle travel in the particle’s frame of reference? TOPIC : GENERAL PHYSICS 2 // TIME DILATION AND LENGTH CONTRACTION.arrow_forward
- A. Two balls move as shown in the figure. (Figure 1) What is the speed of ball 1 in a referece frame that moves with ball 1? u = B. What is the direction of ball 1 in a referece frame that moves with ball 1? left, right, the ball is at rest C. What is the speed of ball 2 in a reference frame that moves with ball 1? D. What is the direction of ball 2 in a reference frame that moves with ball 1?arrow_forwardI am struggling with getting the following done and would greatly appriciate some help, pls explain and mnake sure your answer is correct 100% pls and thank you Answer the following parts for the relativity Question Part A. An electron has a total energy of 5.8×105eV. What is its speed? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Part B Derive an expression for the speed of a particle of rest mass m0 in terms of its total energy E. Part C What is the speed of a particle if its total energy is equal to twice the rest mass energy?arrow_forwardFor part c), how come we cannot use the relativistic momentum equation where p = mv/(sqrt(1-v^2/c^2))? Since we've already solved for velocity in part b)?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
