
Concept explainers
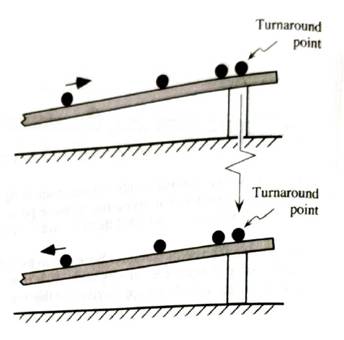
Choose a point before the turnaround and another after.
In the space below, draw the velocity vectors and label them
Draw the vector that must be added to the velocity at the earlier time to obtain the velocity at the later time.
Is the name change in velocity that you used in sections I and II also appropriate for this vector?
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 1 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
College Physics (10th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
Conceptual Integrated Science
Introduction to Electrodynamics
- Suppose a projectile is fired with initial speed v, and angle e above the horizontal. a) Understand and plan. Draw a picture, establish a coordinate system for this problem and label your diagram. Make a table of known/given information and unknown/wanted information (this may involve reading the rest of the problem before starting). b) Using Kinematics, derive a symbolic expression for the maximum height reached by the projectile. Check the physical units of your expression. c) Using Kinematics, derive a symbolic expression for the total time the projectile is in the air. Check the physical units of your expression. d) Using Kinematics, derive an expression for the magnitude and direction angle of the projectiles velocity a time t after the object is fired. Check the physical units of your expression. e) Suppose that the projectile is fired with an initial speed of v, = 46.6 m/s and 0 = 42.2°, what is the magnitude and direction angle of the projectile's velocity t = 1.50 s after…arrow_forwardPart C Based on the vector diagram in Part B, determine how far downstream of your starting point you will finally reach the opposite shore if the stream is 6.0 meters wide. ▾ View Available Hint(s) Hint 1. Find the time to cross the stream Notice that your velocity has been given in component form: 3.0 m/s across the stream and 4.0 m/s along the stream. Based on these velocity components, how long will it take you to cross the 6.0 meter wide stream? Express your answer in seconds. d= VE ΑΣΦ Submit Submit Request Answer 15. ΑΣΦ Provide Feedback Request Answer ? m 2 of 8 (> Next > 9:28 AM 6/19/2018arrow_forwardConstruct Vectors with Lengths Proportional to the Horizontal and Vertical Velocities: The images that follow are motion diagrams created based on a video analysis of the ball’s path. Use the fact that the lengths of displacement and velocity vectors are proportional to each other to draw a series of vectors that are proportional to the average x and y-velocity vector components during each 1/15th of a second time interval. Start with Frame 1 in each of the figures that follow. Place the tail of the first velocity vector at the ball’s location in frame 1 and then place the tail of the next vector at the ball’s location in frame 2 and so on.arrow_forward
- Please help with parts g and h Two velocity vectors are defined as follows: v1 = 40.0 m/s, 50.0 degrees cw from the +x axis v2 = 30.0 m/s, 75.0degrees cw from the -y axis d) Calculate the x- and y-components of v2. Write the vector v2 in terms of its components using unit vector notation. e) Calculate the x- and y-components of the change in velocity defined as Δv= v2-v1. Write the vector Δv in terms of its components using unit vector notation. f) Sketch the vector Δv on an x-y grid. Define a relevant angle symbolically whose numerical value you will calculate in the next part. g) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the vector Δv. h) Finally, write the vector Δv in terms of its magnitude and direction.arrow_forwardYou fire a ball with an initial speed V0 at an angle (ϕ) above the surface of an incline, which is itself inclined at an angle (θ) above the horizontal (Figure below). a. Find the distance, measured along the incline, from the launch point to the point when the ball strikes the incline. b. What angle ϕ gives the maximum range, measured along the incline? Ignore air resistance. c. Since there's no air resistance, this is a problem in projectile motion. The goal is to find the point where the ball's parabolic trajectory intersects the incline. It is best to choose the x-axis to be horizontal and direct to the right, the y-axis to be vertical and direct to the up, and the origin to be at the point where the ball is fired. In the projectile equations, the launch angle α0 is measured from the horizontal. What is this angle in terms of (θ) and (ϕ)?arrow_forwardThis is a two part problem. If you drive your car for 30 miles to the west, then 20 miles north of east at 60 degrees and then 5 miles south: A. What is the displacement of your car from the origin in unit vector notation? Draw a diagram to go along with your answer. B: What is the magnitude and direction of the displacement?arrow_forward
- Two dogs, Ajax and Bandit, are pulling a Radio Flyer wagon carrying their best cat friend, Casper. the overhead view of the dog force vectors is shown to scale in the grid at the right. (Assume 4 significant figures.) a. Find the single force that is equivalent to the two forces shown. b. If that old rusty wagon DOES NOT MOVE, find the force (including direction) that the ground exerts on the wagon to keep it in place, in spite of the dogs. The forces are measured in units of newtons (N). (You may use EITHER geometry OR vector addition with Cartesian or polarcoordinates. Either way, a diagram to scale is required. Be sure to JUSTIFY whyyour answer to part b is the opposite of your answer to part a.)arrow_forwardA diver running 2.1 m/s dives out horizontally from the edge of a vertical cliff and 3.5 s later reaches the water below. Part A How high was the cliff? Express your answer using two significant figures. Part B How far from its base did the diver hit the water?Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardA. From the perspective of point x, vector a and vector b are approaching with around the same speed. From Joseph's perspective, the two are walking with around the same speed. Determine if vector a is approaching with the same speed, twice the speed, or half the speed from the perspective of vector b. Explain.B. Vectors x and y are moving with uniform velocities. If the image below is t = 0, how long will it take (in seconds) for vector x to be in the same position with vector y? How far should vector x have traveled (in meters) by the time it has overtaken the position of vector y? Show proper solution.arrow_forward
- The diagram below is comprised of four vectors A, B. C and D. Using addition and subtraction of vectors, describe the following: D A B Note: your answer should be an algebraic expression comprising of A, B. C and D. Make sure to take note of the positions of the tails and heads of each vector. B = 0 = |(i.e., when you add the vectors together, they cancel and equal 0)arrow_forwardPart B As stated in the strategy, choose a coordinate system where the x axis is horizontal and the y axis is vertical. Note that in the strategy, the y component of the projectile's acceleration, ay, is taken to be negative. This implies that the positive y axis is upward. Use the same convention for your y axis, and take the positive x axis to be to the right. Where you choose your origin doesn't change the answer to the question, but choosing an origin can make a problem easier to solve (even if only a bit). Usually it is nice if the majority of the quantities you are given and the quantity you are trying to solve for take positive values relative to your chosen origin. Given this goal, what location for the origin of the coordinate system would make this problem easiest? At the peak of the trajectory At the point where the rock strikes the ground At the point where the rock is released At ground level below the point where the rock is launched At ground level below the peak of the…arrow_forwardMake a sketch of the trajectory of a ball after it has been thrown. Draw the ball in at least five different positions; two when the ball is going up, two when it is going down, and one at its maximum height. Label the horizontal and vertical axes of your coordinate system. On your sketch, draw and label the expected acceleration vectors of the ball (relative sizes and directions) for the five different positions. Decompose each acceleration vector into its vertical and horizontal components. On your sketch, draw and label the velocity vectors of the object at the same positions you chose to draw your acceleration vectors. Decomposes each velocity vector into its vertical and horizontal components. Check to see that the changes in the velocity vector are consistent with the acceleration vectors.arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
