
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 6.3, Problem 2cT
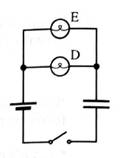
1. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb D compares to the initial brightness of bulb li. Explain.
2. Predict how the initial brightness of bulb 1) compares to the initial brightness of bulbs A, B, and C above. Explain.
3. Predict how the final charge on the capacitor compares to the final charge on the capacitor from part A. Explain.
Set up the circuit and check your predictions. If your prediction is in conflict with your observation, how can you account for your observation?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule07:48
Students have asked these similar questions
1. For all practical purposes, a capacitor is considered fully discharged (or fully charged)
after 5 time constants. What is the voltage across a discharging capacitor in a RC circuit
that has V₁ = 10V, and t = 5 t seconds? Show your work
2.
What is the purpose of finding t in a RC circuit?
3. In the virtual simulation, the light bulb is a nice visual indicator of the behavior of a
discharging series RC circuit. However, explain why is it easier to find C using a resistor
instead of a Light Bulb.
How will the brightness of bulbs A and B change if bulb C is unscrewed?
Will the result be different if bulb D or E is unscrewed instead? Explain.
7. Consider the circuit shown on the right.
Are the bulbs C, D, and E connected
in series, parallel, or neither? Explain.
Parallel b/c the junction point
is above point D where the current spreads
a.
Rank the bulbs in order of bright-
ness. Use the symbols =, .
Explain your ranking.
b.
с.
A 24.0 V battery is wired in parallel with three resistors, R1 = 10.0 Ohms, R2 = 60.0 Ohms, and R3 = 150.0
Ohms.
а.)
circuit including proper symbols and labels. (Do not copy and paste an image from any other resource)
Using either the computer drawing tools or a scanned hand written diagram, draw this
b.)
and label the current flow on your diagram.
Find the equivalent resistance and total current running through the circuit. Show your work
c.)
Find the current flow and voltage drop through each resistor. Show your work and explain.
wer
Chapter 6 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 6.1 - Obtain a battery, a light bulb, and a single piece...Ch. 6.1 - A student has briefly connected a wire across the...Ch. 6.1 - Light a bulb using a battery and a single wire....Ch. 6.1 - Carefully examine a bulb. Two wires extend from...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of the two bulb with each...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of each of the bulbs in the...Ch. 6.1 - We may think of a bulb as percentage an obstacle,...Ch. 6.1 - Compare the brightness of the bulbs in this...Ch. 6.1 - Is the brightness of each bulb in the two-bulb...Ch. 6.1 - Formulate a rule for predicting how the current...
Ch. 6.1 - Does the amount of current through a battery seem...Ch. 6.1 - Unscrew one of the bulbs in the two-bulb parallel...Ch. 6.1 - The circuit at tight contains three identical...Ch. 6.1 - Show that a simple application of the model for...Ch. 6.2 - The circuits at right contain identical batteries,...Ch. 6.2 - The circuits at right contain identical batteries...Ch. 6.2 - Predict the relative brightness of bulbs...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with a single bulb and the...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit containing two bulbs in series...Ch. 6.2 - Predict what the voltmeter would read if it were...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with two bulbs in parallel as...Ch. 6.2 - Answer the following questions based on the...Ch. 6.2 - Set up the circuit with three bulbs as shown and...Ch. 6.2 - Before setting up the circuit shown at right:...Ch. 6.2 - Both circuits al right have more than one path for...Ch. 6.3 - A capacitor is connected to a battery, bulb, and...Ch. 6.3 - Remove the capacitor and the bulb from the...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose an uncharged capacitor is connected in...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that instead of connecting the uncharged...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that the bulbs were connected in parallel...Ch. 6.3 - After completing the experiments above, two...Ch. 6.3 - Suppose that a different capacitor of smaller...Ch. 6.3 - Before connecting the circuit a student makes the...Ch. 6.3 - Make the following prediction on the basis of your...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
11. What is the law of reflection for sound?
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
Q12.28 Airports at high elevations have longer runways for takeoffs and landings than do airports at sea level....
University Physics (14th Edition)
Human Exploration of Mars. Should we send humans to Mars? If so, when? How much would you be willing to see spe...
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Youre working in quality control for a model rocket manufacturer. testing a class-D rocket whose specifications...
Essential University Physics (3rd Edition)
6. (II) Vector is 6.6 using long and points along the negative x axis. Vector is 8.5 units long and points at t...
Physics: Principles with Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the diagram at the right of a parallel circuit. Each light bulb in the circuit has an identical resistance. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. Each question may have one, less than one, or more than one answer. a. The electric potential at point A is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. b. The electric potential at point D is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. c. The electric potential at point J is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. d. The electric potential difference between points A and J is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. e. The electric potential difference between points D and G is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any…arrow_forwardDirection. Answer each problem and show your solutions cleanly and clearly. Draw diagrams. 1. Three capacitors when connected in series gives an equivalent capacitance of 1.2 uF. When they are connected in parallel, the equivalent capacitance is 12.4 uF. The capacitance of the second capacitor is 1.5 times the first. Find the capacitance of each. Three capacitors when connected in series gives an equivalent capacitance of 1.2 uF. When they are connected in parallel, the equivalent capacitance is 12.4 uF. The capacitance of the second capacitor is 1.5 times the first. Find the capacitance of each. Answer: 4, 6, 2.4 uFarrow_forwardConsider the diagram at the right of a series circuit. Each light bulb in the circuit has an identical resistance. Use the labeled points on the diagram to answer the following questions. Each question may have one, less than one, or more than one answer. a. The electric potential at point A is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. b. The electric potential at point C is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. c. The electric potential at point F is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. d. The electric potential at point I is the same as the electric potential at point(s) ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. e. The electric potential difference between points A and B is the same as the electric potential difference between points ___ and ____. Include all that apply, if any apply. f. The electric potential difference between…arrow_forward
- A 12.0V battery is wired in series with 3 resistors, 8 Ohm, 15 Ohm and 75 Ohm. a.) Using either the computer drawing tools or a scanned hand written diagram, draw this circuit including proper symbols and labels. (Do not copy and paste an image from any other resource) b.) Find the equivalent resistance and current flowing through each resistor. Show your work and label your diagram with the current amount and direction of flow. GEind the voltage drop, across each resistor in the circuit. Show your work.arrow_forwardII. Solve for the total voltage, individual voltages, total current, individual currents, total resistance, and individual resistances in each circuit diagram. Write your answers in the table provided beside each circuit diagram and show all HANDWRITTEN solutions in the last page. 1. Type of Connection: VT = 15.0 V R1 = 7.00 2 R2 = 4.00 2 R3 = 2.00 2 VI = I = RT = Vi = R1 = V2 = 12 = R2 = V3 = 13 = R3 =arrow_forwardPart B. Finding the PD Directions: Solve the following problems. Write your answer on a clean sheet of paper. Show your solutions. 1. To carry how much charge between two points having potential difference equal to 220 V, 1760 J of work is done? Ans. 8 C 2. The EMF of a cell falls from 3 volts to 2.8 volts when its terminals are joined to an electrical load of 4 Ohms. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.arrow_forward
- Answer the following questions. 1. Why does the voltage across the resistor for charging and discharging processes change the sign from positive to negative? Hint: think about the direction of current. 2. Does the voltage V across the resistor for charging and discharging obey by the same equation: V = Vo eRC 3. What is the sum of the voltages across the capacitor Vc and across the resistor VR at any point in time during the charging and discharging processes? Use a snipping tool to copy and paste the waveform chart and graph for the charging and discharging curves into the lab report.arrow_forwardTwo 60.0 Ω resistors are connected in parallel and this parallel arrangement is then connected in series with a 30.0 Ω resistor. The combination is placed across a 120. V potential difference. 1.Draw a schematic diagram of the circuit using correct symbols. 2.What is the equivalent resistance of the parallel portion of the circuit? 3.What is the equivalent resistance for the entire circuit? 4.What is the total current in the circuit? 5.What is the voltage drop across the 30.0 Ω resistor? 6.What is the voltage drop across the parallel portion of the circuit? 7.What is the current through each resistor?sarrow_forward2. Combinations of capacitors. You have three capacitors, 3 μF, 6 μF, and 9 μF. a. What is the equivalent capacitance if they are connected in series? Show your work. b. What is the equivalent capacitance if they are connected in parallel? Show your work.arrow_forward
- A 24.0 V battery is wired in parallel with three resistors, R1 = 10.0 Ohms, R2 = 60.0 Ohms, and R3 = 150.0 Ohms. a.) Using either the computer drawing tools or a scanned hand written diagram, draw this circuit including proper symbols and labels. (Do not copy and paste an image from any other resource) b.) Find the equivalent resistance and total current running through the circuit. Show your work and label the current flow on your diagram. c.) Find the current flow and voltage drop through each resistor. Show your work and explain.arrow_forwardCircuit Practice 1. Find the total resistance when the following resistors are connected in series a. 2.7 Ω, 9.8 Ω b. 10 Ω, 10 Ω, 103 Ω 2. Find the total resistance when the following resistors are connected in parallel a. 4.0 Ω, 4.0 Ω b. 100 Ω, 100 Ω 3. Based on your answers to practice problems 2, state a rule that could be used to determine the total resistance when two resistors of equal size are connected in parallel. 4. Starting with the equation for resistors in parallel, prove that for two resistors R₁ and R₂, the equivalent total resistance R, is: 4000 5. In the circuit shown to the right Vab = 4.0 V, la = 2.0 A, and R₁ = 2.002. Find the values of the following: a. Ic b. Voc 1: (a) R₁ = 6.0 2 b. la 9.0 V R 6. In the circuit shown to the right l = 2.0 A and I = 3.0 A. Find the values of the following: a. Vbd = R₂ = 200 R_R₂ R₁+R₂ R₁ = 300 c. RT c. RT 7. For each of the circuits shown below, find the current through and the potential drop across each resistor. R₂=300 R₁ = 100 1₂…arrow_forwardDirections: Write the letter of your answer on a separate sheet of paper.1. With 21 V applied, if R1 = 5 ohms, R2 = 35 ohms, and R3 = 14 ohms, whatis the current in R2 if R1 is connected in series with the parallel circuit R2and R3?A. 200 mA B. 400 mA C.600 mA D.800 mA 2. What is the total resistance of a circuit when R1 (7 kΩ) is in series with aparallel combination of R2 (20 kΩ), R3 (36 kΩ), and R4 (45 kΩ)?A.4 kΩ B.17 kΩ C. 41 kΩ D. 108 kΩarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Series & Parallel - Potential Divider Circuits - GCSE & A-level Physics; Author: Science Shorts;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vf8HVTVvsdw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY