
Concept explainers
The diagram at right illustrates what an observer sees when looking at two boxes on a large table.

From the diagram alone:
• is it possible to determine which box is closer to the observer?
• is it possible to determine which box appears wider to the observer?
• is it possible to determine which box actually is wider?
Discuss your reasoning with your partners.
To determine whether the two boxes closer and wider.
Answer to Problem 1aT
Yes, it is possible to determine whether the boxes are closer and wider. Box A is closer to the observer than B. And box B is wider than A.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
- When an object is closer it looks brighter as the light reflected from the object travel lesser path before it enters into the eye. Whereas the light reflected from the object placed travels greater distance, thus the intensity of light entering into eyes is less.
- Also, objects at greater distance appear to be smaller than the ones kept near. For example, Sun is 100 times bigger than Earth and still appears smaller.
- Figure 1: As the Box A is brighter compared to the box Bi, t is closer to the observer. Box A is closer as it looks brighter due to the less pathtraveled by the light reflected from the Box A before it reaches the observer. On the other hand, the light reflected from the Box B travels greater distance, thus the intensity of light reaching the observer is less and consequently appears darker.
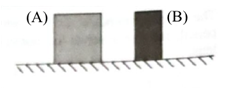
Figure 1: Two boxes (A) and (B)
- As it is clear from the Figure 1, box A looks wider compared to box B.
- Yes, it is possible to determine the which box is actually wider by comparing the intensity of light compared to the source light. As the intensity of light decreases inversely to the square of the distance. The contrast between the two reflected light from the two boxes will determine the distance and from the distance one can determine how the size of the object decreases with the distance.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
University Physics Volume 2
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
- Hi can you solve the question plz? and make brief explanation, ( plz if you are gonna use handwrite pls make sure that is clearly readable) question 1 and 2 (first 3 options a b c)arrow_forwardEinstein’s Postulates• State and explain both of Einstein’s postulates.• Explain what an inertial frame of reference is.• Describe one way the speed of light can be changed.arrow_forwardRemaining Time: 29 minutes, 42 seconds. v Question Completion Status: L A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 1 "For the oscilloscope, if there are 10 divisions on the horizontal scale, then time window will be" Horizontal scale factor x 10Nivisions Horizontal scale factor + 10 divisions Horizontal scale factor None of these 5A Moving to another question will save this response. U Assignment2_2018.pdf Double-wishbone-..jpg 81A5TJZNNXL_SL1. FL21 P..arrow_forward
- Problem 10 A dog can live 8 years. You want to see your dog when you are at 100 years old. And you are 20 years old currently. There is many ways to elongate life of your dog. And one of them is your dog travel near speed of light and dilate some time. Consider minimum and assume you don't have to see it for 80 years, How fast does your dog has to travel in term of speed of light to see your dog at 8 years old? First, calculate Lorentz factor.arrow_forward"I think light sometimes behave like a particle". Explain why you believe your statement is correct. How would you convince your classmate who disagree with the statement? Use all relevant observation from the class activities and your own observations to justify your argument.arrow_forward(multiple choice) The equation E = kq/r2 applied to (explain why that answer is correct): a. all objects b. any spherical objects c. it applies to all objects as long as they are not moving d. any symmetric e. only pointlike particlesarrow_forward
- Physics *DO NOT COPY AND PASTE. Beyond what you have done with Bending Light/More Tools Simulation, make few new findings such changing medium, or give real life examples for bending light. You can express your findings by data table, word, equations, and/or screenshot graph/Video, but do giving physics explanation. You could also design meaningful experiment and show it here. In Part C minimum 10 sentences are required.arrow_forwardhi please solve the following question, please note more than one or all options can be correct, please provide the correct answer with a detailed explanation i will rate you.arrow_forwardthe handwritten in the whiteboard is the information given and please explain how did you get b^2=a^2(1-e^2) and ed=a(1-e^2) to solve question no 2barrow_forward
- Challenges to Space Exploration a) We can round numbers to say light (and all electromagnetic radiation: radio waves, infrared, ultraviolet, etc.) travels at approximately 3x108 m/s. At its closest approach, Mars is about 0.5 au of the Earth. At this distance, how long would it take for an astronaut on Mars to communicate with Mission Control on Earth? Give your answer in minutes. Explain why Mars rovers have entire sequences for travel pre-programmed and uploaded all at once rather than being driven around in real time with a joystick. For the Earth-Moon distance in 5b, you can use 384,400 km b) The boosters that launched Apollo 11 allowed the astronauts to reach a speed of 25,000 miles per hour. At that speed, about how long did it take for the astronauts to reach the Moon? At that speed, how long would it take to reach Mars, assuming the closest approach distance given above? Give your answers in days.arrow_forwardHi can you solve the question 1 and 2 plz? and make brief explanation, ( plz if you are gonna use handwrite pls make sure that is clearly readable) question 1 and 2arrow_forwardPoint M moves between two points A and B, that a are 10 meters apart, with speed v=2 m/s. For each position of M we consider the equilateral triangles AMG and MBD A) Find the sum of areas of the two triangles as a function of time t B) For which time t is the area defined by question A the minimum and what is that minimum area C) In which position of the point M we have the minimum area D) What is the rate of change of Area when the distance AM=8marrow_forward
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
