
Concept explainers
(a)
The current induced in the aluminum ring
(a)
Answer to Problem 5P
A current of
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the emf generated in the coil.
Here,
Here,
Write the equation for the magnetic field due to the solenoid.
Here,
Substitute
Write the equation for the area of the coil.
Here,
Substitute equation (VI) in equation (V).
The ring is placed at one end of a solenoid. The field in the end of the solenoid is half the field at the center of the solenoid. Write the equation for the emf induced in the ring.
Substitute
Write the equation for the current induced in the ring.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the current induced in the ring is
(b)
The magnitude of magnetic field in the ring
(b)
Answer to Problem 5P
The induced current produces a magnetic field of
Explanation of Solution
Write the equation for the magnetic field produced in the ring.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the induced current produces a magnetic field of
(c)
The direction of magnetic field in the ring
(c)
Answer to Problem 5P
The magnetic field in the ring points towards the left
Explanation of Solution
Figure (I) shows the direction of the magnetic field in the solenoid.
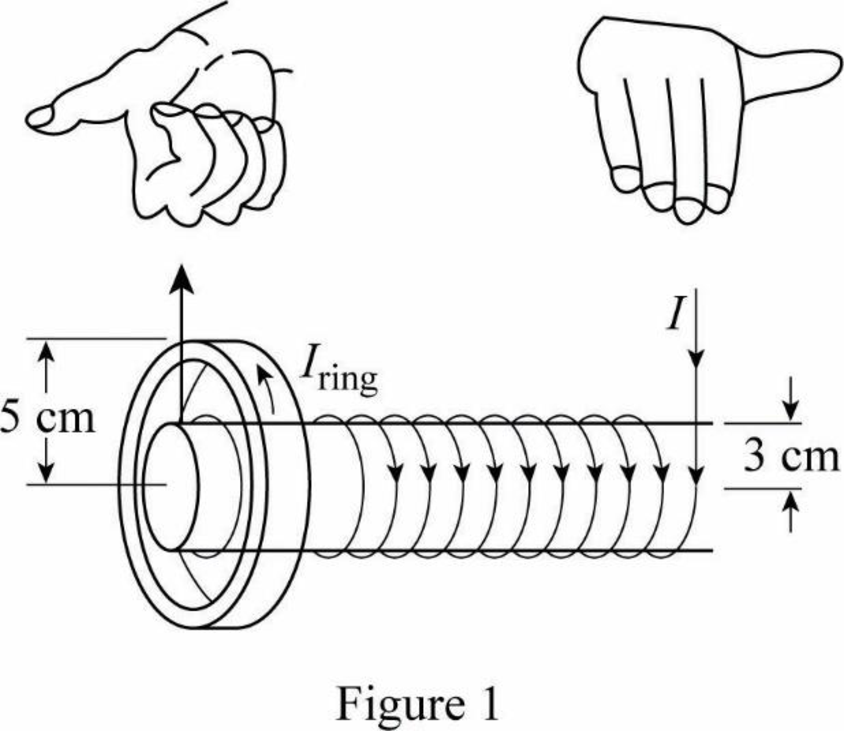
The magnetic field of the solenoid points to the right as shown in figure.1. Therefore, the magnetic field at the center of the ring acts towards the left in order to oppose the increasing field.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnetic field in the ring acts towards the left.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
- An aluminum ring of radius r1 = 5.00 cm and resistance 3.00 104 is placed around one end of a long air-core solenoid with 1 000 turns per meter and radius r2 = 3.00 cm as shown in Figure P30.5. Assume the axial component of the field produced by the solenoid is one-half as strong over the area of the end of the solenoid as at the center of the solenoid. Also assume the solenoid produces negligible field outside its cross-sectional area. The current in the solenoid is increasing at a rate of 270 A/s. (a) What is the induced current in the ring? At the center of the ring, what are (b) the magnitude and (c) the direction of the magnetic field produced by the induced current in the ring? Figure P30.5 Problems 5 and 6.arrow_forwardA solenoid has a ferromagnetic core, n = 1000 turns per meter, and I = 5.0 A. If B inside the solenoid is 2.0 T, what is for the core material?arrow_forwardA piece of insulated wire is shaped into a figure eight as shown in Figure P23.12. For simplicity, model the two halves of the figure eight as circles. The radius of the upper circle is 5.00 cm and that of the lower circle is 9.00 cm. The wire has a uniform resistance per unit length of 3.00 Ω/m. A uniform magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the plane of the two circles, in the direction shown. The magnetic field is increasing at a constant rate of 2.00 T/s. Find (a) the magnitude and (b) the direction of the induced current in the wire. Figure P23.12arrow_forward
- Why is the following situation impossible? A conducting rectangular loop of mass M = 0.100 kg, resistance R = 1.00 , and dimensions w = 50.0 cm by = 90.0 cm is held with its lower edge just above a region with a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 1.00 T as shown in Figure P30.34. The loop is released from rest. Just as the top edge of the loop reaches the region containing the field, the loop moves with a speed 4.00 m/s. Figure P30.34arrow_forwardThe magnetic field at the center of a solenoid L = 65 cm long is B = 0.42 T when a current of I = 3.5 A flows through the solenoid wire. Part (a) Solve the formula for the magnetic field near the center of a long, tightly wound solenoid for the number of turns, N, in the solenoid. The expression should be in terms of the given variables. Part (b) Calculate the value of the number of turns, N.arrow_forwardA very long solenoid with tightly wound coils has8.00 * 10^3 turns of wire per meter of length. What must the current bein the solenoid in order for the field inside the solenoid to have magnitude0.0320 T?arrow_forward
- A long thin solenoid has 808 turns per meter and radius 3.00cm. The current in the solenoid is increasing at a rate of 60A/s. What is the magnitude of the induced electric field (in V/m) at a point near the center of the solenoid and 0.8cm from its axis?arrow_forwardA long thin solenoid has 779 turns per meter and radius 2.00cm. The current in the solenoid is increasing at a rate 23 A/s. What is the magnitude of the induced Electric field (in V/m) at a point near the center of the solenoid and 1.3 cm from its axis?arrow_forwardAn air-core solenoid with 66 turns is 8.00 cm long and has a diameter of 1.20 cm. When the solenoid carries a current of 0.740 A, how much energy is stored in its magnetic field in µJ?arrow_forward
- A solenoid with 1200 turns per meter has a diameter of 5.00 cm. A current I = 2.57 A flows in the counterclockwise direction in the solenoid. A rectangular loop of length L = 16.0 cm, width w = 12.5 cm, and 2 turns is centered on the axis of the solenoid. P (a) Find the magnitude of the magnetic flux through the loop. Wb W (b) When the current is increased to 5.39 A, the magnitude of the induced emf in the rectangular loop is 116 mV. How long did it take for the current to get to this value? ms (c) What is the direction of the induced current in the rectangular loop as viewed from the location P? O counterclockwise clockwise O no currentarrow_forwardA nonconducting sphere has mass 80.0 g and radius 20.0 cm. A flat, compact coil ofwire with five turns is wrapped tightly around it, with each turn concentric with thesphere. The sphere is placed on an inclined plane that slopes downward to the left(Fig. P29.69), making an angle 0 with the horizontal so that the coil is parallel to theinclined plane. A uniform magnetic field of 0.350 T vertically upward exists in theregion of the sphere. (a) What current in the coil will enable the sphere to rest inequilibrium on the inclined plane? (b) Show that the result does not depend on thevalue of θ.arrow_forwardFor a technical application, an electrical engineer needs to create a solenoid using copper wire with diameter d = 0.500 mm. The resistance of the solenoid needs to be 3.30 N and the magnetic field of the solenoid with a current of 2.90 A should be 5.10 × 10-2 T. Assume the resistance does not change significantly with temperature, and the radius of the solenoid is 1.00 cm. (Use p = 1.70 x 10-8 n:m for the resistivity of copper.) (a) How many turns of wire does the electrical engineer need? turns (b) Determine the required length (in cm) of the solenoid. cmarrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



