
Concept explainers
For a two-dimensional Ising model on a square lattice, each dipole (except on the edges) has four “neighbours”—above, below, left, and right. (Diagonal neighbors are normally not included.) What is the total energy (in terms of
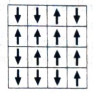
Figure 8.4. One particular state of an Ising model on a
Total energy in terms of
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
Draw a diagram to show one Ising model on
Here, each dipole has four nearest neighboring dipoles except dipoles on edges.
The lattice in above diagram has 14 nearest neighboring dipoles in between parallel dipoles as well as 19 neighboring dipoles in between anti-parallel dipoles in total.
Write the expression of total interaction energy
Simplify the above expression
Conclusion:
Thus, the total energy is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Starting from the N(p) expression of a 3D conductor, derive an expression for the exact density of states D(E) for the 3D conductor in the below graph (You have to show all the steps that lead to your final answer). The length of the conductor is given as L = 20 nm and the diameter is given as D= 4 nm. The +E.. 2mo energy momentum relationship is given as: E =arrow_forwardFor a unit cell with the set of real crystal lattice vectors a1 = (9.96,0,0) a2 = (5.58, 12.7,0) az = (-1.31, -4.33,4.75) Calculate the dot product of the real and reciprocal lattice vectors: a1 b2 Report your result to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardThe intensities of spectroscopic transitions between the vibrational states of a molecule are proportional to the square of the integral ∫ψv′xψvdx over all space. Use the relations between Hermite polynomials given in Table 7E.1 to show that the only permitted transitions are those for which v′ = v ± 1 and evaluate the integral in these cases.arrow_forward
- For Problem 9.18, how do I determine part A & B? This is from a chapter titled, "Electron Spin." This chapter is part of quantum mechanics.arrow_forwardThe dispersion relation for a one dimensional monatomic crystal with lattice spacing a, which interacts via nearest neighbor harmonic potential is given by: w=A Asin (), where A is a constant of appropriate unit. The group velocity at the boundary of the first Brillouin zone is: A. 0 B. 1 C. D. 2 Aa² 2 www. Aq² QUESTION 24 For a diatomic linear chain, the phonon dispersion relation (k) has two branches corresponding to + and sign respectively: 1 1 (M₁₂ + M₁₂) ± P | (M₁ + M₁₂ 1 There are two atoms in the unit cell with masses and M2 and the force constant of nearest neighbor interaction is F and the effective mass, sound will be: A) NA B) = 2 C) a M₁ + M₁ 2(M₁+M₁) w(k) = f M₁ + M₁ 2 4 M₂)²³ - M₁M₂ M₁M₂ M₁+M₂ sin² (29/1/² is kept constant. The velocity ofarrow_forwardQ.3 a) Which type of molecules exhibit infra-red spectra? Calculate the vibrational energy and force constant of 'H"F if its vibrational frequency is 3.0 x 1014 Hz. b) Prove that the eigenvalues of a Hermitian operator are real.arrow_forward
- The simple mass on a spring is the basis for our description of almost any oscillation. Lets consider the vibrational states of a simple diatomic molecule, say N2. We will model it as two identical masses connected by a spring as shown in the figure at the top right.This is a little different from the cart on a spring since there is no wall -- both of the atoms are moving. But if we only look at oscillations of the molecule where the center of mass is not moving, the atoms are moving equally and oppositely. When one is going left, the other goes an equal amount to the right and vice versa. This is like two carts attached to a wall and oscillating equally and oppositely as shown in the lower picture. The only difference is the way we treat the spring. When each atom moves a distance x, the spring between the atoms actually stretches a distance 2x, so the force on each atom is -2kx. We can therefore model the motion of one of the nitrogen atoms as a single cart on a spring if we…arrow_forwardHow "density of states" is defined and used in physics? Draw (schematically) the number of occupied energy levels for Fermi Dirac statistics, Maxwell Boltzmann statistics, and Bose Einstein statistics.arrow_forwardPr. 5. Calculate the force between the two atoms in the diatomic hydrogen molecule that has the following potential: V(x)=(x-xo)²-Vo. Where Vo is the binding energy and ro. 6 are constant parameters.arrow_forward
- The Morse potential The harmonic potential, V(x) = ½kx?, is useful start for modelling molecular vibrations, but it has limitations. A realistic potential between to atoms should accurately represent the sharp increase in the potential as two nuclei come in close proximity, and also have the ability for a bond to break: that is, an asymptote V →0 as x →00. One option, as shown in the figure, is the Morse potential: V(r) = D(1 – e-«(r=re))2 15 10 10 15 20 The parameter D is the well depth (or binding energy) of the potential, re is the bond length, and a is the anharmonicity constant.arrow_forwardDraw Ewald sphere in reciprocal lattice space (k-space) and show clearly by draw the incident wave vector, Ko, scattered wave vector, K , vector G and direction of lattice plane, that a reciprocal lattice point ( 3,-1) is one of the valid point for constructive interference. Briefly explain why (3,-1) lattice is valid point. Is it the reciprocal lattice point not on the surface of the sphere is valid point? Why?arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is correct .1 :for the Bravais lattice The three primitive vectors that form the Bravais lattice are not necessarily O perpendicular to each other b. All lattice points (or lattice sites) and the corresponding atoms are not necessarily equivalent and of the same kind c. It is a typical two dimensional lattice that can be generated by any two .vectors d. Bravais lattice is an infinite array of discrete points with an arrangement and orientation that appear the same no matter from whichorientation you look at .it e. Answers (a) and (d) are correctarrow_forward
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
