
Concept explainers
The uniform bars AB and BC each weigh 4 lb/ft. Calculate the tension in cable DE, and the magnitudes of the ball-and-socket reactions at A, B, and C.
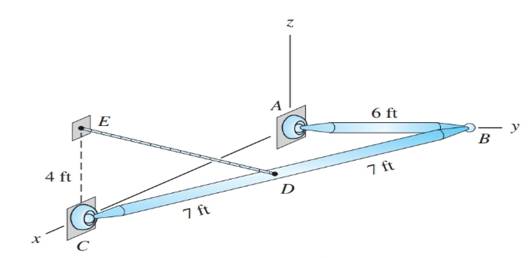
Tension in cable DE and magnitude of reactions at A, B and C.
Answer to Problem 5.56RP
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
Weight of the uniform bars AB and BC is 4 lb/ft.

Calculation:
Draw free body diagram of as shown in following figure,
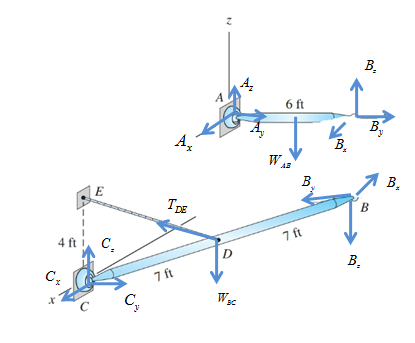
Take equilibrium of moments about x-axis passing through A in free body diagram of AB as,
Take equilibrium of moments about z-axis passing through A in free body diagram of AB as,
Take equilibrium of forces in x-direction in free body diagram of AB as,
Take equilibrium of forces in y-direction in free body diagram of AB as,
Take equilibrium of forces in z-direction in free body diagram of AB as,
Take equilibrium of moments about C in free body diagram of BC as,
Above vector equation yields following scalar equations,
Solve equations 6 and 7 to get
From equation (4)
Take equilibrium of forces in free body diagram of BC as,
Above vector equation yields following scalar equations,
Substitute known parameters and solve equations (8-10) to get,
Magnitude of reaction at A:
Magnitude of reaction at B:
Magnitude of reaction at C:
Conclusion:
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
- The 350-lb homogeneous plate has the shape of an isosceles triangle. The plate is supported by a thrust hinge at A, a slider hinge at B, and the cable CD. Find the force in the cable and the magnitudes of the hinge reactions.arrow_forwardThe uniform, 20-kg bar is placed between two vertical surfaces. Assuming sufficient friction at A to support the bar, find the magnitudes of the reactions at A and B.arrow_forwardThe cable supports three 400-lb loads as shown. If the maximum allowable tension in the cable is 900 lb, find the smallest possible sag hC at C.arrow_forward
- The uniform bar of weight W is held in equilibrium by the couple C0. Find C0 in terms of W, L, and .arrow_forwardThe 180-lb homogeneous bar is supported by a ball-and-socket joint at A and two cables attached to B. Determine the forces in the cables.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a three-pin arch. Determine the horizontal component of the pin reaction at A caused by the applied force P.arrow_forward
- The walkway ABC of the footbridge is stiffened by adding the cable ADC and the short post of length L. If the tension in the cable is not to exceed 420 lb, what is the smallest value of L for which the 160-lb person can be supported at B?arrow_forwardFind the force P required to (a) push; and (b) pull the 80-lb homogeneous roller over the 3-in. curb.arrow_forwardThe hinge shown is the type used on the doors of some automobiles. If a torsion spring at F applies the constant couple C0=20lbft to member ABF, calculate the force P required to hold the door open in the position shown.arrow_forward
- The 80-lb homogeneous plate is supported by a ball-and-socket joint at A, a slider hearing at B, and the cable CE. A 120-lb vertical force is applied to the corner D. Determine the force in the cable and the magnitude of the bearing reaction at B.arrow_forwardcalculate the tension on cable CD and the reaction on joint B if the weight of the cylinder is 85Narrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
