
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure for each of the given thioesters.
Concept Introduction:
Thioesters are sulfur analogs of esters. The S-alkyl or S-aryl thioester has a carbonyl group and a sulfur-linked alkyl or aryl group. The first part of the name indicates that the alkyl or aryl group has bonded to the sulfur atom. The last part of the name indicates the
Answer to Problem 25.1P
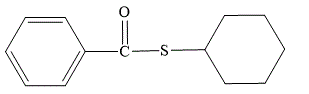
Explanation of Solution
In the given name cyclohexyl thiobenzoate, the cyclohexyl is the alkyl group which is bonded to the sulfur atom. Thiobenzoate consists of a phenyl ring bonded to the sulfur atom through a carbonyl group. The structure for cyclohexyl thiobenzoate is drawn as below:
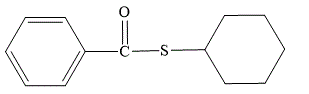
The structure for cyclohexyl thiobenzoate is:
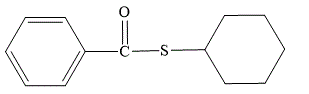
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure for each of the given thioesters.
Concept Introduction:
Thioesters are sulfur analogs of esters. The S-alkyl or S-aryl thioester has a carbonyl group and a sulfur-linked alkyl or aryl group. The first part of the name indicates that the alkyl or aryl group has bonded to the sulfur atom. The last part of the name indicates the carboxylic acid stem. In common usage, the “S-“prefix is understood, and so, it is not mentioned.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
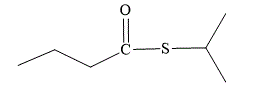
Explanation of Solution
The first part of the name suggests that the isopropyl group must be attached directly to the sulfur atom. The second part of the name suggests that the ester is formed from butanoic acid. In

The structure for S-isopropyl butanethioate is:

(c)
Interpretation:
The structure for each of the given thioesters.
Concept Introduction:
Thioesters are sulfur analogs of esters. The S-alkyl or S-aryl thioester has a carbonyl group and a sulfur-linked alkyl or aryl group. The first part of the name indicates that the alkyl or aryl group has bonded to the sulfur atom. The last part of the name indicates the carboxylic acid stem. In common usage, the “S-“prefix is understood, and so, it is not mentioned.
Answer to Problem 25.1P
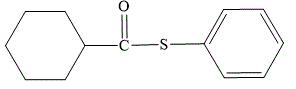
Explanation of Solution
The first part of the name suggests that the phenyl ring must be attached directly to the sulfur atom. The second part of the name suggests that the ester is formed from the carboxylic acid which contains a cyclohexyl ring. In IUPAC nomenclature, “thio-“is inserted before the “ate” suffix in the name of the corresponding oxygen ester.
The structure for S-phenyl cyclohexanecarbothioate is shown as below:

The structure for S-phenyl cyclohexanecarbothioate is:

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Ethyl butyrate, CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3, is an artificial fruit flavor commonly used in the food industry for such flavors as orange and pineapple. Its fragrance and taste are often associated with fresh orange juice, and thus it is most commonly used as orange flavoring.It can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H+): CH3CH2CH2CO2H(l)+CH2CH3OH(l)H+⟶CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3(l)+H2O(l). The chemist discovers a more efficient catalyst that can produce ethyl butyrate with a 78.0% yield. How many grams would be produced from 8.50 gof butanoic acid and excess ethanol? Express your answer in grams to three significant figures.arrow_forwardEthyl butyrate, CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3, is an artificial fruit flavor commonly used in the food industry for such flavors as orange and pineapple. Its fragrance and taste are often associated with fresh orange juice, and thus it is most commonly used as orange flavoring.It can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H+): CH3CH2CH2CO2H(l)+CH2CH3OH(l)H+⟶CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3(l)+H2O(l) a) Given 7.70 g of butanoic acid and excess ethanol, how many grams of ethyl butyrate would be synthesized, assuming a complete 100% yield? b) A chemist ran the reaction and obtained 5.25 g of ethyl butyrate. What was the percent yield? c) The chemist discovers a more efficient catalyst that can produce ethyl butyrate with a 78.0% yield. How many grams would be produced from 7.70 g of butanoic acid and excess ethanol?arrow_forwardEthyl butyrate, CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3, is an artificial fruit flavor commonly used in the food industry for such flavors as orange and pineapple. Its fragrance and taste are often associated with fresh orange juice, and thus it is most commonly used as orange flavoring.It can be produced by the reaction of butanoic acid with ethanol in the presence of an acid catalyst (H+): CH3CH2CH2CO2H(l)+CH2CH3OH(l)H+⟶CH3CH2CH2CO2CH2CH3(l)+H2O(l) Given 8.50 g of butanoic acid and excess ethanol, how many grams of ethyl butyrate would be synthesized, assuming a complete 100%yield? Express your answer in grams to three significant figures.arrow_forward
- Draw compounds that contain the following: (a) A primary alcohol (c) A secondary thiol (c) An isopropyl group (b) A tertiary nitrile (d) A quaternary carbonarrow_forwardDraw the structures of the following compounds:(a) Ethanoic acid(b) Bromopentane(c) Butanonearrow_forwardDraw the structure of the following compounds which parent names have been traced to a common name; (a)5-methyl-4-nitroimidazole (b)2-chloro-4-methoxythiazole.arrow_forward
- Draw a structural formula for the product formed by treating each compound with warm chromic acid, H2CrO4:(a) CH3(CH2)4CH2OH (b) (Picture attached) Please name both of the products, thanks!arrow_forwardThe IUPAC name of the compound is (a) 5-formylhex-2-en-3-one (b) 5-methyl-4-oxohex-2-en-5-al (c) 3-keto-2-methylhex-5-enal (d) 3-keto-2-methylhex-4-enal The correct statement regarding electrophile is (a) electrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from another electrophile (b) electrophiles are generally neutral species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile (c) electrophile can be either neutral or positively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile (d) electrophile is a negatively charged species and can form a bond by accepting a pair of electrons from a nucleophile, Which among the given molecules can exhibit tautomerism? Ph Ph I III (a) III only (b) Both I and III (d) Both II and III (c) Both I and II 5) Which of the following biphenyls is optically active? IIarrow_forwardGive an IUPAC and common name for each of the following naturally occurring carboxylic acids: (a) CH3CH(OH)CO2H (lactic acid); (b) HOCH2CH2C(OH)(CH3)CH2CO2H (mevalonic acid).arrow_forward
- Draw the structure of each compound.(a) o-nitroanisole (b) 2,4-dimethoxyphenol (c) p-aminobenzoic acid(d) 4-nitroanilinearrow_forwardWhat is the major organic product of the following reaction? (a) (b) NaBH4 CH3CH₂OH ? (c) (d) OHarrow_forwardPhenylethanol can be oxidised to phenylethanal or phenylethanoic acid, depending on the reagents used (both the alcohol and the aldehyde are of interest for their antimicrobial properties, while the acid is used to treat type II hyperammonemia): A (a) (b) (c) CoH,CH,CHO phenylethanal B C6H5CH₂CH₂OHC₂H₂CH₂CO₂H phenylethanol Suggest reagents (shown as A and B in the scheme above) that could be used to carry out the oxidation of the alcohol to the aldehyde and the acid, respectively. C6H5CH₂- Suggest two other syntheses of phenylethanoic acid, in each case indicating the starting materials and other reagents required, but not giving details of mechanism. One of your proposed syntheses must start with a compound which only contains seven carbon atoms (the acid product contains eight carbon atoms). phenylethanoic acid Phenylethanal can be converted to a hydrate in the presence of aqueous acid, though the position of equilibrium is very far to the left: H H+/H₂O OH C6H5CH₂-C-H OH Explain why…arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





