
We begin by considering the forces exerted on a ring that is connected to a spring and that is free to slide along a rod. (See the top view diagram at right.)
Assume that the ring is massless and that the rod is frictionless.
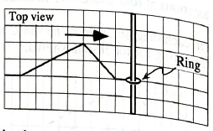
- What is the n, force on the ring? (Hint: Consider what happens to the net force on an object as its mass approaches zero.) Explain.
Does the net force on a massless ring depend on the acceleration of the ring? Explain
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the ring? (Recall that the ring is massless.)

Check that your free-body diagram is consistent with your answers to pans i and ii.
Would your answer above differ if you considered an instant when the free end was not at its farthest point from its equilibrium position? Explain.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 23 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics (10th Edition)
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
- Solve and answer the following question showing the complete step-by-step process. 1. A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make angles θ1 = 60.0 degrees and θ2 = 40.0 degrees with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2, and T3 in the wires.arrow_forwarduse the GRAPHICAL METHOD to solve the given problem below to recall what you have discussed in physics about the head-to-tail rule of constructing vector/force diagrams and about Newton’s 1st Law of motion.An electric light fixture weighing 15 N hangs from a point C, by two strings AC and BC. The string AC is inclined at 60° to the horizontal and BC at 45° to the horizontal as shown, determine the forces in the strings AC and BC.1. What scale did you use?2. What is the force in string AC?3. What is the force in string BC?arrow_forwardGive me right solution according to the question Note: Diagram not given. A 1kg block is placed at an inclined sloped at 10 degrees with the horizontal and is pushed up by a 150N force for 3 seconds from which then the 150N force is then removed. The block will continue sliding upward due to is momentum until it will completely stop. How far has the block traveled? if the coefficient of friction is 0.3 between the block and the inclined plane.arrow_forward
- Consider the information in the image below. Write the net force equation the axis perpendicular to the plane . Then solve for the normal force in terms of the weight of the box, mgand the angle of inclination, such as mg cos(?) Make it clear on your diagram how the angle is used in finding force componentsarrow_forwardA mirrored sphere, weighing 200.0 N is suspended from the ceiling of a ballroom by two cables as shown in the diagram. What is the tension in each of these cables? ... 45° 30° Type your solution and answer here or upload the picture of your written solutions and answers. Use the editor to format your answerarrow_forwardThe figure below depicts a ball in flight. The direction of the airflow is indicated by the stack of straight arrows pointing to the right towards the ball. The linear velocity of the ball is indicated by the vector, VB. The curved arrow represents the direction of rotation of the ball. What direction will the Magnus force act (i.e., which direction will the ball be pushed due to its interaction with the fluid flow)? Ⓒa. Right → O b. Up ↑ O c. Left - O d. Down ↓ VBarrow_forward
- The class I'm taking is physics for scientists and engineers! *** I need help with parts D and E only*** I have attached the problem below! Please view attachment before answering. If you can please explain your answer so I can fully understand. Thank you so so much!arrow_forwardDirection: Show your free body diagram, formula, solution, and box your final answer. Upload your file here. A block of weight W=100 N is on a rough plane inclined at an angle of 30' with the horizontal. 30 30 W=100 N W=100 N Calculate 1. The magnitude of the normal force N1 and the friction F1 when the block is in equilibrium as shown in figure 1. 2. If the plane was frictionless, find the magnitude of the horizontal force F1, required to keep the block in equilibrium as shown in figure 2.arrow_forwardProvide a brief solution in problem in the picture below.In picture below, there's an answer key for the problem. So, your answer from a to g must be the same in an answer key provided below. Thank you in advance.arrow_forward
- The previous step focused on friction for horizontal surfaces. As we discussed above, angled surfaces like the wedge below have different considerations. FN = mg cos(0) F₁ = mg F₁ = ? F₁ = ? Fy=mg cos(0) Specifically, we have the following considerations. 1. The normal force is not equal to mg. 2. There is a force acting along the angle of the wedge due to gravity. What is the coefficient of static friction ? Fx = mg sin(0) Let's consider the implications of this type of problem with the following examples. For all of the examples, the box has a mass of 25 kg. Imagine the box is on a surface that allows you to adjust the incline angle, 0. You find the maximum angle where the box remains stationary. That is, at any higher angle, and the box begins to slide. The static friction force at this maximum angle is 150 N. What is the angle 0 (in degrees)? Now you raise the incline to an angle of 60° greater than the angle of maximum static friction found above. At this angle, the box slides…arrow_forwardThe center of the Ferris Wheel is 36 feet above the ground. The wheel has a 32 foot radius and is turning at 30 degrees per second. a.) Write an expression for all times that the person is 20 ft above the ground and descending. b.) Graph two complete periods of your function and label with ordered pairs, all points on your graph where the person is 20 feet above the ground and descending.arrow_forwardClick on the image below to launch the video: Unfair Race. Once you have watched the entire video, answer the graded follow-up questions on the right. You can watch the video again at any point. PEARSON reset ALWAYS LEARNING This video shows the results of releasing a frictionless box and a rolling disk with equal masses from the top of identical inclined planes. Part B How much sooner does the box reach the bottom of the incline than the disk? Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables m, h, 0, and R, as well as the acceleration due to gravity g. ► View Available Hint(s) ΨΗ ΑΣΦ/Φ Submit Previous Answers ? X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





