
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130970695
Author: Peter S. Shaffer, Lillian C. McDermott
Publisher: Addison Wesley
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.1, Problem 1aT
Draw arrows on the diagram to represent the direction of the velocity for each of the points A, 13, and C at the instantshown. Explain your reasoning.
Is the time taken by points B and C to move through one complete circle greater than, less than, or the same as thetime taken by point A?
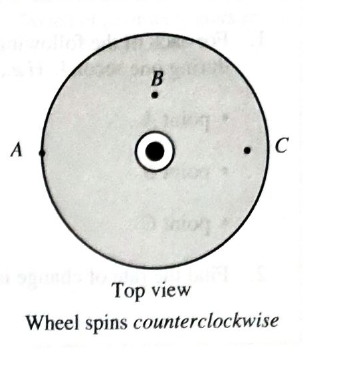
On the basis of your answer above, determine how the speeds of points A, B, and C compare. Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A. From the perspective of point x, vector a and vector b are approaching with around the same speed. From Joseph's perspective, the two are walking with around the same speed. Determine if vector a is approaching with the same speed, twice the speed, or half the speed from the perspective of vector b. Explain.B. Vectors x and y are moving with uniform velocities. If the image below is t = 0, how long will it take (in seconds) for vector x to be in the same position with vector y? How far should vector x have traveled (in meters) by the time it has overtaken the position of vector y? Show proper solution.
The statements in the following list all refer to the description of motion. Check the boxes
of the THREE TRUE statements.
1. If a particle moves along a straight line with an acceleration that is always equal
to zero, it has a constant velocity.
2. If a stone is launched horizontally with initial speed u from the top of a tower of
height 7, the time taken for the stone to strike the ground is roughly proportional to u.
3. The acceleration vector of a particle in uniform circular motion is perpendicular to
the velocity vector and points radially outwards.
4. If a particle moves round a circle of radius 2.0 m with an angular speed of
3.0 rad s-¹, it has a linear speed of 6 m s-¹.
5. The amplitude of the oscillation for an object undergoing simple harmonic motion
increases when its initial phase increases.
6. If an unpowered satellite travels in circular orbit around the Sun with an orbital
radius that is 4 times greater than the semimajor axis of the Earth's orbit, the satellite
will…
The figure shows three paths taken along the horizontal axis. Each path begins at the circular dot beneath the letter denoting the path's name and ends at the very tip of the arrow. In your calculations, round to the nearest integer.
A. What is the distance traveled, in meters, for path C?
B. What is the magnitude of the displacement from start to finish, in meters, for path C?
C. What is the displacement from start to finish, in meters, for path C?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Tutorials in Introductory Physics
Ch. 4.1 - Draw arrows on the diagram to represent the...Ch. 4.1 - Mark the position of each of the labeled points at...Ch. 4.1 - Suppose the wheel makes one complete revolution in...Ch. 4.1 - Would two observers on either side of a rotating...Ch. 4.1 - The diagrams at right show top and side views of...Ch. 4.1 - In the space at right sketch the position vectors...Ch. 4.1 - Let | in terms of |o| . 1. The wheel is made to...Ch. 4.1 - Suppose the wheel slows down uniformly, so that ||...Ch. 4.1 - A force of magnitude Fo is applied to point M as...Ch. 4.1 - Compare the magnitude of the net torque about the...
Ch. 4.2 - A ruler is placed on a pivot and held at an angle...Ch. 4.2 - Draw a free-body diagram for the ruler (after it...Ch. 4.2 - How would your free-body diagram change if the...Ch. 4.2 - Predict: which spool will reach the floor first....Ch. 4.2 - Obtain two spools and a ring stand. Use the...Ch. 4.2 - Consider the following discussion between three...Ch. 4.2 - Write down Newton’s second law for each spool....Ch. 4.3 - A T-shaped board of uniform mass density has two...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 1bTCh. 4.3 - Attach day to the bottom left side of the board so...Ch. 4.3 - Prob. 2bTCh. 4.3 - C. Imagine that the T-shaped board (with no clay...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
3. What is free-fall, and why does it make you weightless? Briefly describe why astronauts are weightless in th...
The Cosmic Perspective
Express the unit vectors in terms of (that is, derive Eq. 1.64). Check your answers several ways Also work o...
Introduction to Electrodynamics
35. || Bio Human biomechanics. World-class sprinters can spring out of the starting blocks with an acceleration...
College Physics (10th Edition)
71. Phosphate ions, PO43-, were once added to detergents to assist in cleaning. What function did they serve? T...
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
52. You are target shooting using a toy gun that fires a small ball at a speed of 15 m/s. When the gun is fire...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A plane flying at 78.2 m/s [W32°S] takes 42 seconds to change its velocity to 78.2 m/s [S32°E]. a) Solve for the change in velocity of the plane algebraically, resolving vectors into their x- and y-components. b) What was the average acceleration of the plane over this time interval? c) Explain why the speed of the plane didn't change and yet the plane underwent acceleration. Please label sketches with events as well as GRASS and explanations to show your work. Please label triangle sides. Remember to have the magnitude rounded to a reasonable number of sig figs, the unit and the direction (if needed) in your answers.arrow_forwardA gardener walks in a flower garden as illustrated in the figure below. What distance does the gardener travel?m A coordinate plane has a horizontal axis labeled Distance (meters) and a vertical axis that is also labeled Distance (meters). A garden path is drawn on the coordinate system, and four arrows represent the path the gardener walks. The arrows are as follows:From (0,6) to (2,6),from (2,6) to (2,5),from (2,5) to (4,5),and from (4,5) to (4,3).arrow_forwardA particle travels with velocity v= (8m/s^2) t-7m/s. A.)find the average acceleration for two 1-s intervals, one beginning at t=3s and the other beginning at t=4s. B.)sketch v versus t. What is the instantaneous acceleration at any time? Please show your complete solution and answer all. write your solution clearly and readable. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Consider an object moving along the circular trajectory r(t) = (A cos wt, A sin oot), where A and are constants. Answer parts a through e. a. Over what time interval [0,T] does the object traverse the circle once? The interval is [0]. (Simplify your answer. Type an exact answer using as needed.)arrow_forwardPart C What is the line integral B-dl for the path c? The integral involves going around the path in the counterclockwise direction. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO AE T.m Submit Request Answer Part D What is the line integral B-dl for the path d? The integral involves going around the path in the counterclockwise direction Express your answer using two significant figures. T.m மொர். Request Answer Provide Feedback 84 Farrow_forwardA cannon is turned towards the west and a cannonball is fired. This cannonball has a velocity of 252 kmph at an angle 60 degrees. The cannonball lands on a hillside 100 metres above its starting level. What is the range of the cannon ball? Make a simple sketch. Make a list of all given values, units, and the variables they represent. write the general form of the equation you are going to use. Insert the known values and solve. State at the start of the problem which direction is positive by using an up or down arrow. Keep the velocity components and time to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Show your solution. Two cars, 100 apart, are about to collide. The cars, X & Y, are running at constant speed of 60kph &80 kph, respectively. a.) Illustrate the velocity vectors of the cars and formulate the equations. b.) What is the speed (in kph) of car Y observed on car X? c.) How many seconds will they collide?arrow_forwardQuick description In this lab you will study two-dimensional motion, specifically projectile motion. You will roll a ball down an inclined plane (a track with one end propped). The ball will fly off the end of the inclined plane and undergo projectile motion until it hits the ground. At the moment the ball is leaving the inclined plane, a photogate detector measures the time the ball takes to pass through the gate. Using the diameter f the ball and the photogate time, you can calculate the speed of the ball when it passed through the photogate. Based on the angle of the inclined plane, the initial speed for the projectile motion, and the distance the ball falls (Ay in figure), you should be able to predict the horizontal distance (Ax in figure) and compare it to your measured horizontal distance. 41cm Ball 121cm Inced Plane Table Inclined plane angle = sin ^-1 (41cm/121 cm) = 19.81° Ball diameter = 0.013 m Delta Y= 76 cm=0.76 m Time (s) Velocity (m/s) Delta X (m) 0.00707 0.184 0.654…arrow_forwardA child rides a pony on a circular track whose radius is 4.5 m.(a) Find the distance traveled and the displacement when the child has gone halfwayaround the track.(b) How does the distance traveled change while the child completes one circuit of thetrack? Explain.(c) How does the displacement change while the child completes one circuit of thetrack? Explain.(d) Find the distance and displacement after a complete circuit of the track.arrow_forward
- An object is thrown into the air and returns to the ground. The equation relating height and time for this object is , where h is the height in meters and t is the time in seconds. In which form is the quadratic function expressed? Justify your answer. Find the zeros or t-intercepts of this function. Explain their significance. Write the function in standard form Find the co-ordinates of the vertex. Is this vertex a maximum or minimum? Explain the significance of this point?arrow_forwardI need to make sure I have the correct answers. can you please show the steps for the problem #16 ( attached pictures). thanks you.arrow_forwardI Review You are riding on a Jet Ski at an angle of 35° upstream on a river flowing with a speed of 2.8 m/s. Part A If your velocity relative to the ground is 9.5 m/s at an angle of 20.0° upstream, what is the speed of the Jet Ski relative to the water? (Note: Angles are measured relative to the z axis shown in (Figure 1).) Express your answer in meters per second to three significant figures. Ubw = m/s Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next > Figure wg "bg=9.5 m/s wg =28 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON
Vectors and 2D Motion: Crash Course Physics #4; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w3BhzYI6zXU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY